Cyberattacks, data leaks, hacking…these cyber threats are a reality for all companies, regardless of their size. So, how can we effectively protect ourselves against these risks? This is where the international standard- ISO/IEC 27001 comes in, which establishes a solid framework to protect companies’ sensitive data.
What is ISO/IEC 27001?
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard, developed jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), provides a methodological framework for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It helps organizations identify, assess, and address risks related to information security, whether digital or physical.
Initially published in 2005, this standard was revised in 2013 and then in 2022. The latest version, “ISO/IEC 27001:2022”, takes into account recent developments in the digital world, such as the development of remote working and the increased use of cloud services.
Why is this standard essential?
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard allows:
- Data protection: It guarantees confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
- Risk reduction: Identifies and controls risks to help prevent security breaches.
- Customer trust: Standard certification strengthens company’s credibility and assures their customers that shared data is handled securely.
- Competitive edge: Differentiates your organization by showing adherence to globally recognized standards.
What are the differences between the 2017 and 2022 ISO/IEC 27001 standard versions?
The 2022 revision brings significant adjustments. This version aims to improve readability and better reflects current issues:
- Simplification and reorganization of measures:
The 114 measures of the 2017 version – were reduced to 93 in 2022, of which 82 -were merged or reformulated, and 11 new security measures were added.
The measures were organized into four main themes:
- People Control: Safety related to individuals.
- Physical Controls: Protection of physical objects and infrastructures.
- Technological Controls: Covers technological devices and systems.
- Organizational Controls: Includes all other measures.
- New attributes to classify measures:
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 also highlights five types of attributes to facilitate the identification and classification of measurements:
- Control type: Preventive, detective or corrective.
- Information security properties: Confidentiality, integrity and availability.
- Cybersecurity concepts: Identify, protect, detect, respond, or recover.
- Operational capabilities: Enriched and modernized from the old themes of Annex A (e.g. governance, human resources security, asset management, etc.).
- Security domains: Governance and ecosystem, protection, defense and resilience.
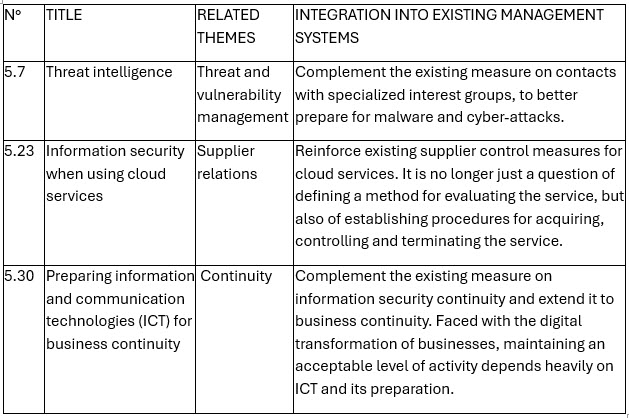
11 new security measures of the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard
ISO 27001:2022 introduced 11 new controls in Annex A to address today’s cybersecurity challenges better. These measures take into account new data protection regulations (GDPR compliance, e-Invoicing Decree, CCPA, etc.), the digital transformation of businesses, and the intensification of cyber threats. They include requirements for protecting cloud environments and business continuity in the event of a crisis. Here are some of the security measures integrated into the standard:
How to obtain ISO/IEC 27001 certification?
ISO/IEC 27001 certification is based on a structured process for implementing and validating an Information Security Management System (ISMS). Here are the main steps a company follows to obtain this certification.
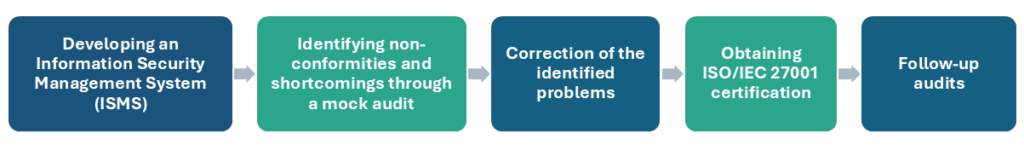
1. Developing an Information Security Management System (ISMS)
The process begins with the creation of an ISMS. This includes:
- Defining the organization’s security objectives and policies.
- Identifying, assessing and prioritizing risks to implement appropriate measures.
- Document security management practices to describe how the ISMS operates.
2. Identifying non-conformities and shortcomings through a mock audit
Once the ISMS is in place, it is crucial to conduct a white audit (or internal audit). This exercise allows:
- To assess the effectiveness of the ISMS and its compliance with the requirements of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.
- To identify gaps, weaknesses or failures related to the required criteria.
- To test the maturity of security processes and ensure that practices are operational.
3. Correction of the identified problems
After the white audit, the detected non-conformities must be corrected. This step includes:
- Implementation of corrective actions to address gaps.
- Improving security processes and measures.
- Validation of changes made to ensure that they meet the standard’s requirements.
This is an iterative process aimed at strengthening system compliance.
4. Obtaining ISO/IEC 27001 certification
If the audit is conclusive, an accredited body issues the certificate attesting to the conformity of the ISMS.
- This certification is valid for 3 years, after which it can be renewed.
5. Follow-up audits
To maintain certification and ensure the sustainability of the ISMS, an accredited third-party body must conduct a certification audit.
- Regular surveillance audits: A full initial audit is conducted in the first year, followed by follow-up audits in the following two years to verify continued compliance.
- A continuous improvement process: this process ensures that the ISMS remains relevant and effective in the face of changing risks.
Symtrax has achieved ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification
Symtrax is now ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certified! This international certification attests to our commitment to ensuring the security and confidentiality of all our customers’ data. Our software solutions now comply with the highest international standards, enabling our customers to experience a reliable and secure digital environment.
You can consult our press release on this subject.
