In the digital age, continuous innovation is practically mandatory. Staying innovative ensures your business complies with the latest regulations while increasing efficiency to ultimately ensure business continuity. According to a survey, 90% of businesses claim legacy systems are hindering their technical advancement.
Many enterprises still use legacy systems and are not ready to retire them yet. But does this mean they will lag in the race for efficiency? A Statista report predicts that global spending on digital transformation will rise up to $3.4tn by 2026. Is there a way to reap the benefits of going digital while still putting legacy systems to use?
In this blog, we will discuss how to leverage digitization without scrapping legacy systems with the aid of “middleware.” This technology can bridge the gaps in digital transformation and empower legacy systems with modern-day digitization capabilities.
What is middleware?
A middleware is a medium to facilitate seamless data or information transfer across multiple applications. This can involve varying formats, connectivity, or software versions. More specifically, middleware is a software application that can be installed on an on-premise server, in the cloud, or even accessed in your computers. It serves as the underlying framework that links disparate applications, data, and users.
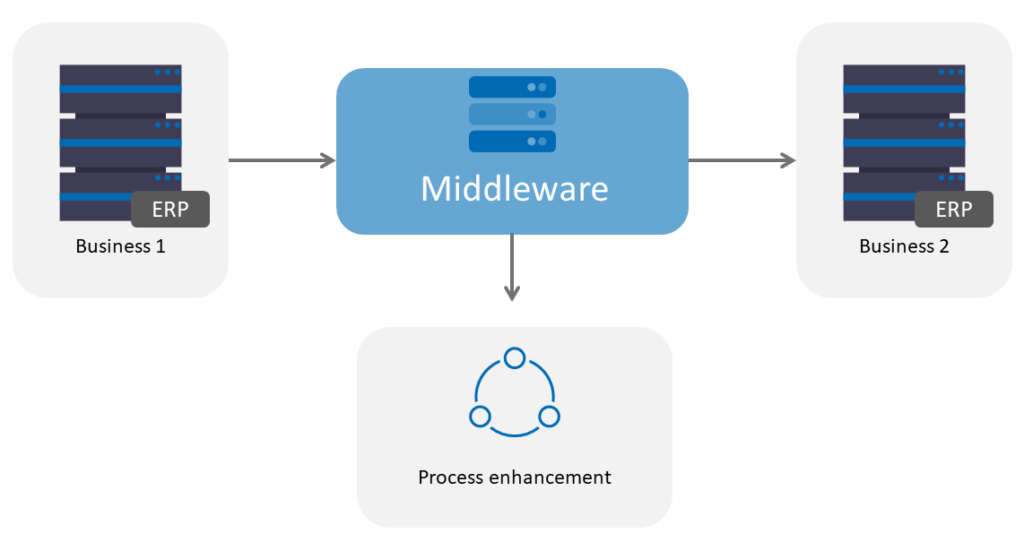
The Benefits of middleware
Middleware can be a solution to any legacy system hurdles faced while embarking on digital transformation. Here are some of the promising benefits businesses can look at when considering investing in middleware (The list is not exhaustive: you can read more about the financial and strategic benefits of such an approach here):
- A cost-effective approach – Middleware can be a versatile digital transformation solution, allowing businesses to upgrade gradually while eliminating bottlenecks. They even provide the possibility of adopting one solution at a time, enabling enterprises to financially plan for system upgrades.
- Quick adoption– Middleware helps businesses accelerate digital adoption initiatives. Just by installing a basic application / software, it becomes possible to access multiple modern features. There are minimal requirements, thus allowing for easy integration of most systems, if not all.
- Security– Since middleware acts as a company’s intermediary software, it has to adhere to all compliance measures. Not only is it able to do this, it can also automatically adapt to changing requirements.
- Scalability– Middleware can accommodate all your needs as your business grows, reducing the rigidity of legacy systems. Because it’s installed on a separate environment, upgrades and scaling activities do not affect the node itself or the entire business. Load balancers, processing power scaling, and other technologies are readily available to provide minimal downtime while enhancing overall efficiency and deployment turnaround.
- A completely digital partner eco–system: Middleware empowers enterprises to provide a digital platform to business partners using a secured channel. Find out how here.
How Middleware Works
Middleware can be seamlessly integrated via different types of connections, such as local folders, ERP Output, and other Electronic Data Transfer methods. As per business needs, documents can be modified, translated, and transformed into the desired format. These can then be transported to the specified recipient by different forms of messaging methods/protocols.
Here are some examples of middleware in play:
SCENARIO 1: Business 1 wishes to automatically generate files for Business 2
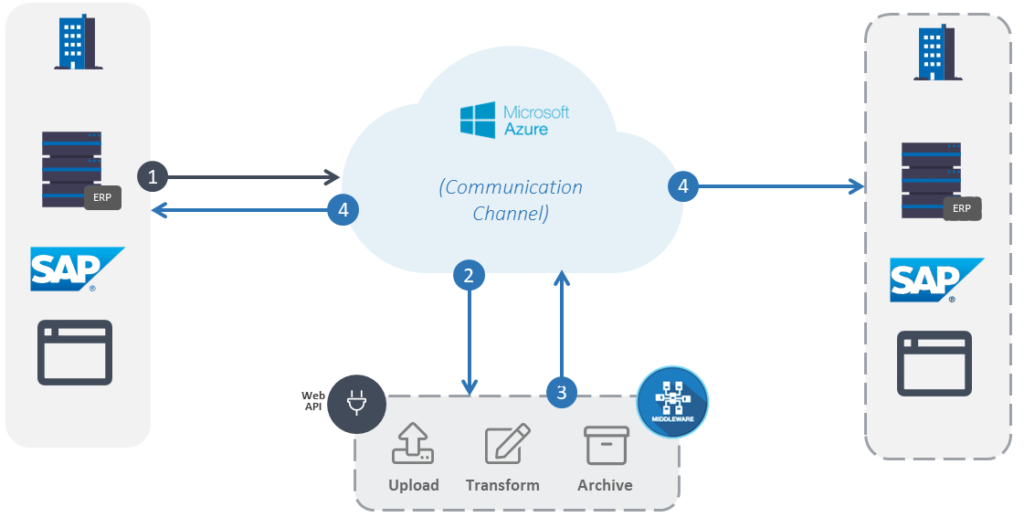
Business 1 can export its data via various methods and send it to the cloud. There, the middleware can pick up the data and proceeds to upload and retrieve more information, transform the data and layout, and archive the original data. The middleware then pinpoints Business 2 as a recipient and proceeds to arrange the file to be distributed to them. All this can occur without involving Business 1 in any document post-processing.
SCENARIO 2: Business 1 wishes to submit an e-invoice via Peppol
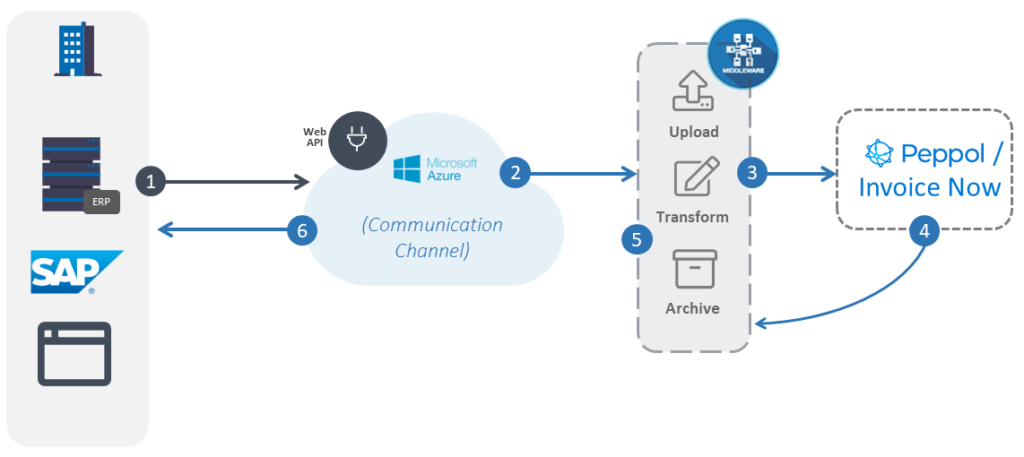
The middleware in this scenario is in-charge of transforming the data retrieved from Business 1. It converts it into a format depicted by InvoiceNow or Peppol before sending it through the gateway. Upon doing so, the gateway should send a response, which the middleware then transforms by for Business 1 to read. Business 1 does not need to have or produce the correct format here and can use whatever available information they might have. Gain insights on integrating with Peppol here – This methodology works for InvoiceNow as well!
SCENARIO 3: Externally integrate additional services into current systems
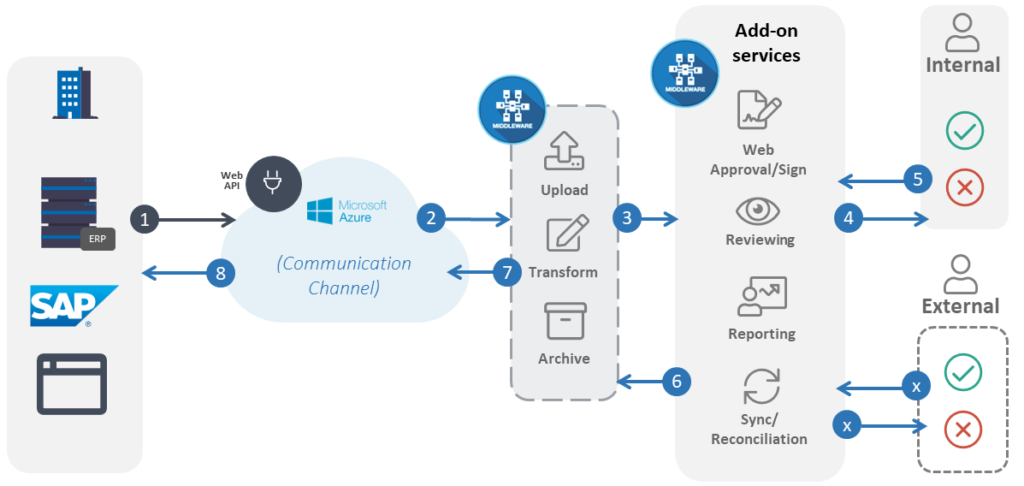
In addition to querying external entities such as Peppol, middleware can incorporate add-on services. Much like what we see in Compleo Hybrid, your middleware solution can contain features such as web approval, reviewing, reporting, external reconciliations, automation or workflow. These features can all seamlessly assist with internal or external. See how enterprises have been integrating these middleware add-on services here.
Learn more about the details of digitization using middleware and its technicalities in our next blog.
If you have a topic you want us to cover, feel free to reach out to Solution Expert.


