It’s impressive to witness the Malaysian government taking significant strides towards modernization with the new E-Invoicing regime.
As we discussed the details of Malaysia E-invoicing Guidelines in our previous blog, lets now explore the latest updates and steps to issue compliant e-invoices in Malaysia. This will set as the foundation for a streamlined and efficient implementation process for your business.
Important Update on Malaysia E-Invoicing
The Malaysian government and IRBM have granted a six-month grace period for LHDN E-Invoice Reporting to help businesses adjust to the new mandate. The grace period starts from August 1, 2024, lasting until February 1, 2025, for businesses > 100 million revenue. However, Malaysian businesses still have to issue consolidated e-invoices during this period.
Step-By-Step Guide: Malaysia E-Invoicing
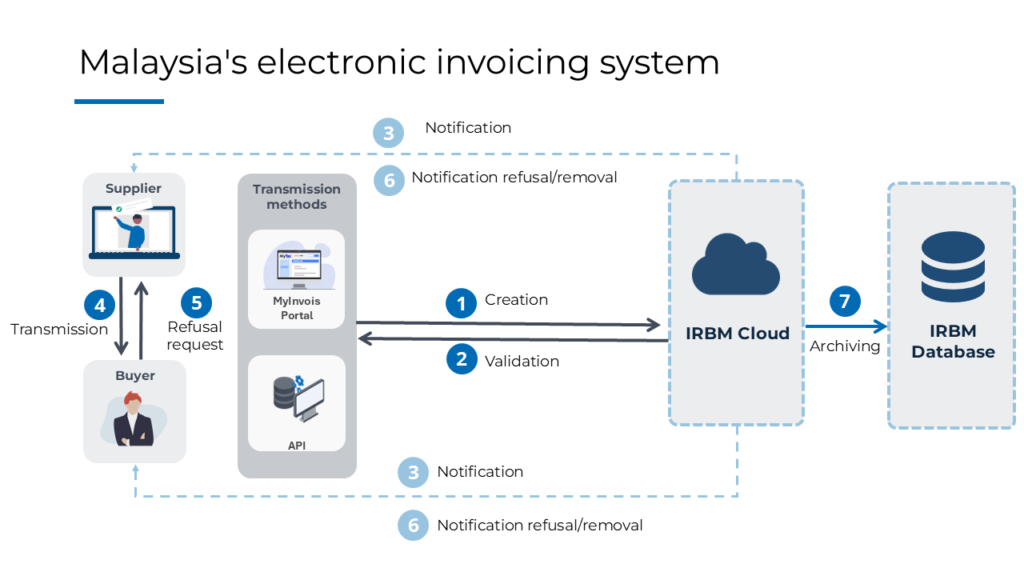
The process of submission, validation and issuance of e-invoices in Malaysia can be understood by the following simplified steps:
Step 1: Creation
When a transaction/sale is made, the supplier creates an electronic invoice in XML or JSON format and transmits it to the IRBM via the MyInvois portal or via API for validation.
Step 2: Validation
The IRBM validates the e-invoice in real-time, ensuring that it complies with the required standards and criteria.
Once the invoice has been validated, the supplier receives a Unique Identifier Number (UIN) from the IRBM, either from the portal or via API. This identification number allows IRBM to guarantee the traceability of all invoices, eliminating the chances of forgery.
Step 3: Notification
IRBM then informs the supplier and the buyer that the sent e-invoice has been validated via the MyInvois portal or by API.
Step 4: Transmission
The supplier is obliged to send the validated e- invoice (with QR code embedded) to the buyer. This QR code is used to certify the existence and status of the invoice via the MyInvois portal.
Step 5: Opt-out or deletion
Once the invoice has been sent, it is possible within a specified period (72-hour window):
- For the buyer to request the rejection of the invoice.
- For the supplier to cancel the invoice.
These requests must be accompanied by supporting documents.
Step 6: History
Finally, the supplier and the buyer can access the history of all transactions carried out by them on the MyInvois portal anytime.
Correction Window (If required)
Once the invoice has been validated by IRBM, both the supplier and buyer have an option to cancel or reject the e-invoice.
1- Buyer requests the rejection of e-invoice via API
- If errors are present in the invoice, the buyer can request its rejection within 72 hours from the date of validation via API.
- The rejection request must include the Unique Identifier Number (UIN) of the invoice as well as the reason for rejection that may contain incorrect information (e.g. sales and service tax registration number, company registration number, etc.).
- When the buyer initiates the rejection request, a notification is sent to the supplier.
- If the supplier accepts the justification provided by the buyer, e-invoice is then entitled for cancellation within 72 hours. If the supplier refuses the buyer’s request for rejection, no cancellation is possible.
2- Supplier cancels the e-invoice via API
- If the invoice contains errors or has been issued in error, the supplier may cancel it within 72 hours from the date of issue of the invoice.
- In case of cancellation, a notification is sent to the buyer. The supplier will then have to issue a new electronic invoice.
Note: If the invoice is not rejected or cancelled within 72 hours, no cancellations will be allowed. Any changes require the issuance of a new electronic invoice.
Storage of Electronic Invoices
All electronic invoices will be stored in the IRBM database. However, it should be noted that this storage method will not be considered the only option. Malaysian businesses have to continue setting up their own archiving system in accordance with the IRBM regulations in force.
What are the prerequisites before sending an e-invoice?
Companies must first configure their IT systems or choose a solution that allows them to generate compliant e-invoices, in XML or JSON format, and including all mandatory and additional fields.
Digital Signature
Every e-invoice needs to be authenticated by a digital signature of the authorized signatory of the business. The use of a digital certificate (type .cer or .pfx) that validates the issuer of the e-invoice is essential. This digital signature guarantees the origin and integrity of the invoice issued.
IRBM has specified that both Soft and Roaming certificates can be used for MyInvois purpose, depending on the company’s system configuration. A Soft certificate is installed in local machine, while the Roaming certificate is installed in Server/HSM.
Conclusion
Understand that being precise with information and staying updated with recent changes is essential. Partnering with reliable solution providers like Symtrax simplifies this process, providing the necessary tools and support to meet IRBM/LHDN guidelines effectively. By following mentioned steps, your business will not only run more smoothly but also stay in line with the new digital era.


